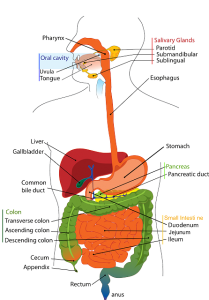
What is the purpose of gallbladder? During the process of digestion, gallbladder’s role is to store the bile, concentrate and release afterwards. All of the chemicals in solution of the bile is thought to be retained but usually one of them turns into crystals and forms into a sandy like type of particles which turns into gallstones. Once the gallstones formed, this causes gallbladder disease which is called cholelithiasis.
After they moved about, sooner or later, the outlet is blocked and prevents the gallbladder from emptying once the bile crystals combined to form stones. Irritation, inflammation and sometimes infection (cholecystitis) of the gallbladder are the results of the blockage. Because of the stones moving in and out of the way, the outline is usually one of erratic hindrance. On the other hand, the gallbladder becomes more and more damaged or scarred. One serious complication is sometimes the gallbladder is infected because it is filled with pus.
In some occasion, gallstone will move down the cystic duct into the common bile duct and get trapped there. This will make back bile up into the liver as well as the gallbladder because of the blockage. Once the stone get stuck at the ampulla of Vater, the pancreas will also be blocked and pancreatitis is developed.
A sudden onset of pain in the upper abdomen is caused by gallstones. The pain will be felt for 30mins up to several hours. This pain may also be felt in the upper abdomen. The person who suffers from this will also experience nausea with or without vomiting may go with the pain.
The Treatment
The usual best treatment of the removal of the total gallbladder with all the stones formed is by surgery. With the use of laparoscope, it is noted that quicker recovery has been the result and much smaller surgical incisions however, not everybody is a candidate for this method. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy is executed if the procedure is not probable to have hitches.
ERCP – endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatoscopy procedure permits the removal of some bile duct stones through the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, and biliary system minus the need for operating incisions. Provided that a finely detailed pictures are available, ERCP can also be used to inject distinction agents into the biliary system.
Furthermore, apart from physical examination to gallstone diagnosis, preparation for laboratory (blood) and special tests is essential. To envision the gallbladder and associated structures, patients with biliary colic may have raised bilirubin and should have an ultrasound check. For the both acute cholecystitis and cholangitis, an increase in the white blood cell count (leukocytosis) can be expected.
ERCP is the test usually indicated to assist in a definitive diagnosis for both choledocholithiasis and cholangitis while Ultrasound testing is recommended for acute cholecystitis patients. Elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy is used to treat either biliary colic or choledocholithiasis whichever the patient has. For acute cholecystitis open cholecystectomy is recommended. Emergency ERCP is indicated for stone removal for cholangitis case. Produced by gallbladder disease ERCP therapy can remove stones.
Post-operative care
Stones rarely occur without a gallbladder. A need for an ERCP to detect residual stones or damage to the bile ducts caused by the original stones for patients who have continued symptoms after their gallbladder is removed. Rarely, is too tight for bile to flow through and causes symptoms until it is opened up the ampulla of Vater.
Threats on the Treatment
Cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder, is the most common medical treatment for gallstones. Damage to the bile ducts, residual gallstones in the bile ducts, or injury to the surrounding organs can all occur although risks associated with gallbladder removal are low.
As a patient, it is important that you are well informed of the risks and consequences of these procedures so as your patient’s right is not violated. Call Us for Free ERCP consultation.